# Code Execution
Supports executing Python, JavaScript, PHP, Golang, LUA, and Shell scripts using either a local native virtual machine (such as a local Python environment) or an integrated system virtual machine that does not rely on the local environment.
# Input
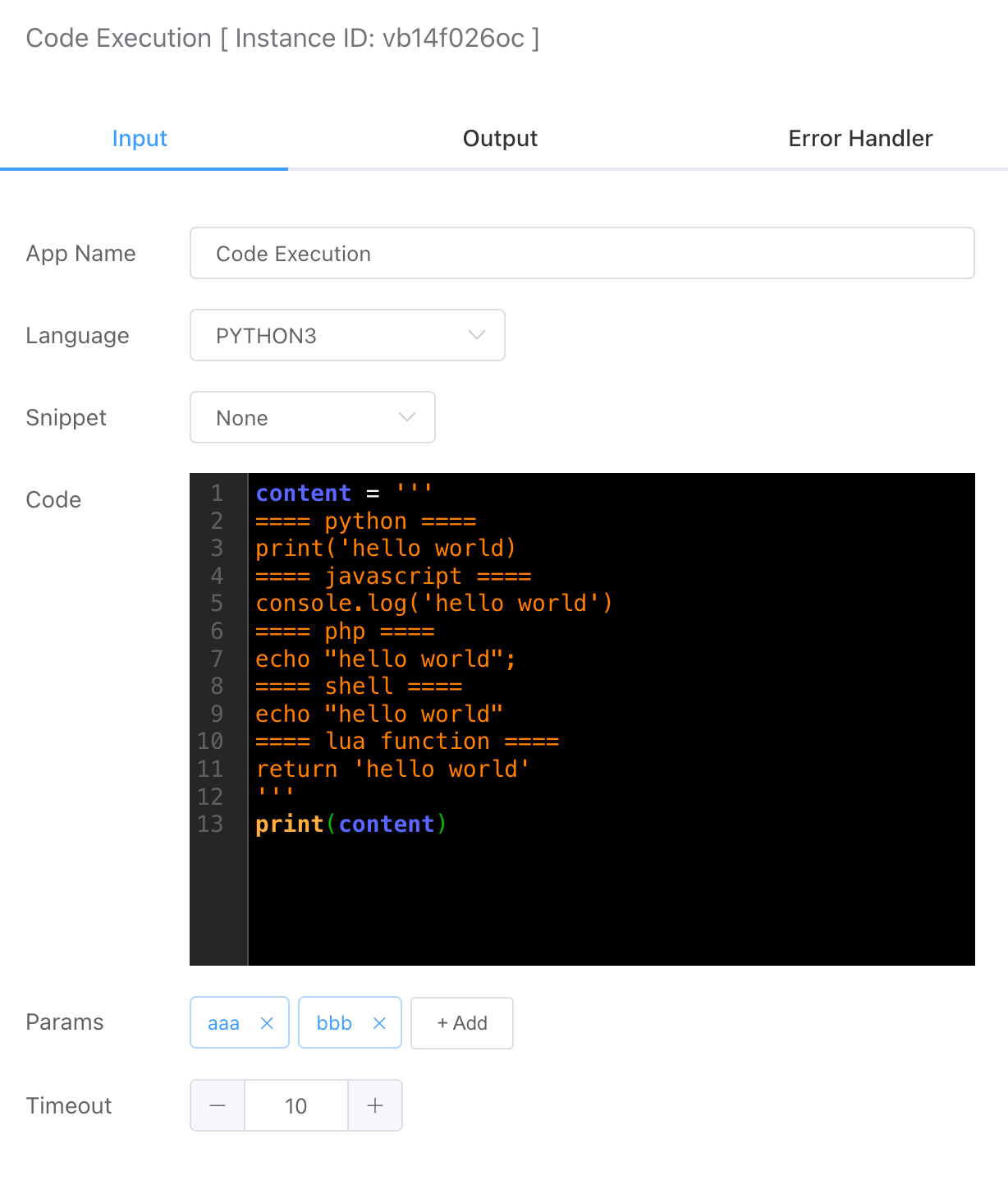
# Language
Local Native Virtual Machine
- Python3
- PHP
- LUA
- SHELL
Note: The local native virtual machine depends on the current machine environment; if the corresponding virtual machine is not available, the script cannot be executed.
Built-in Virtual Machine
- JavaScript
- LUA
- Go
Note: The built-in virtual machine does not depend on the local environment and can execute scripts directly.
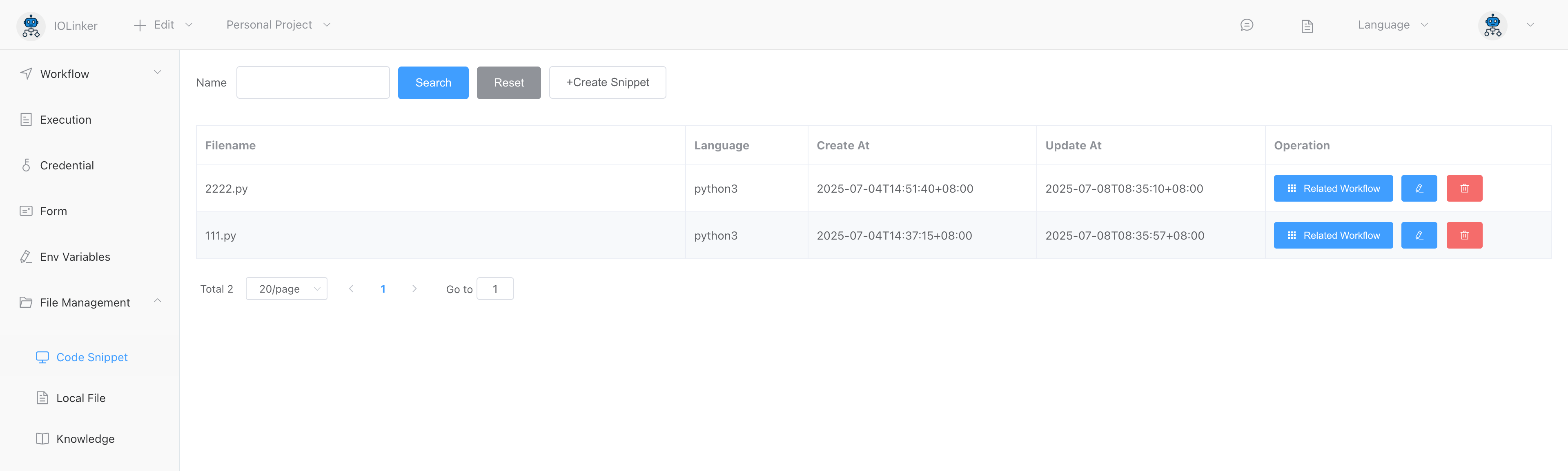
# Snippet
Code snippets will be displayed under the corresponding programming language list in File Management -> Code Files.
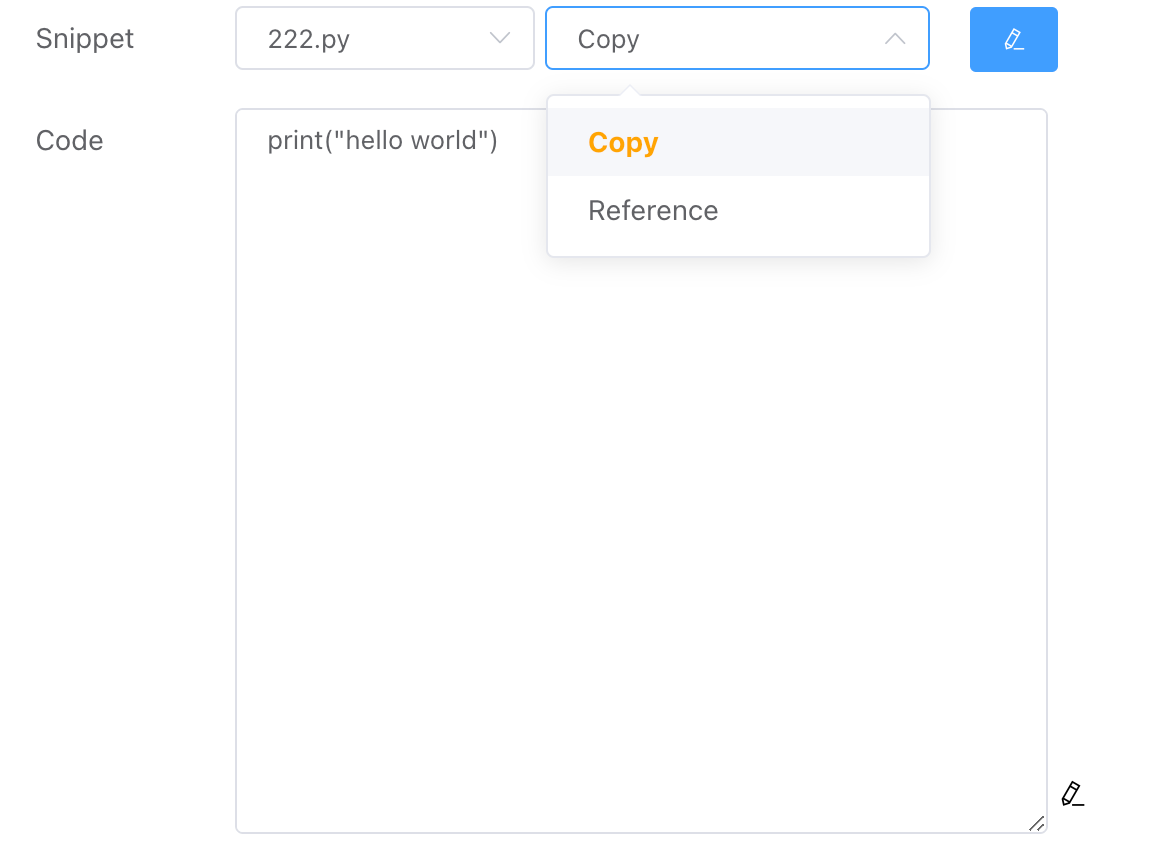
For the selected code files, two types of operations are supported:
Copy
This operation will create a copy of the currently selected code, allowing modifications to this code without affecting the original referenced code.
Reference
This operation references the selected code, which can only be opened for editing and modification in the Code Snippet section.
In the code editor under Code Snippet, you can write code and debug it simultaneously:
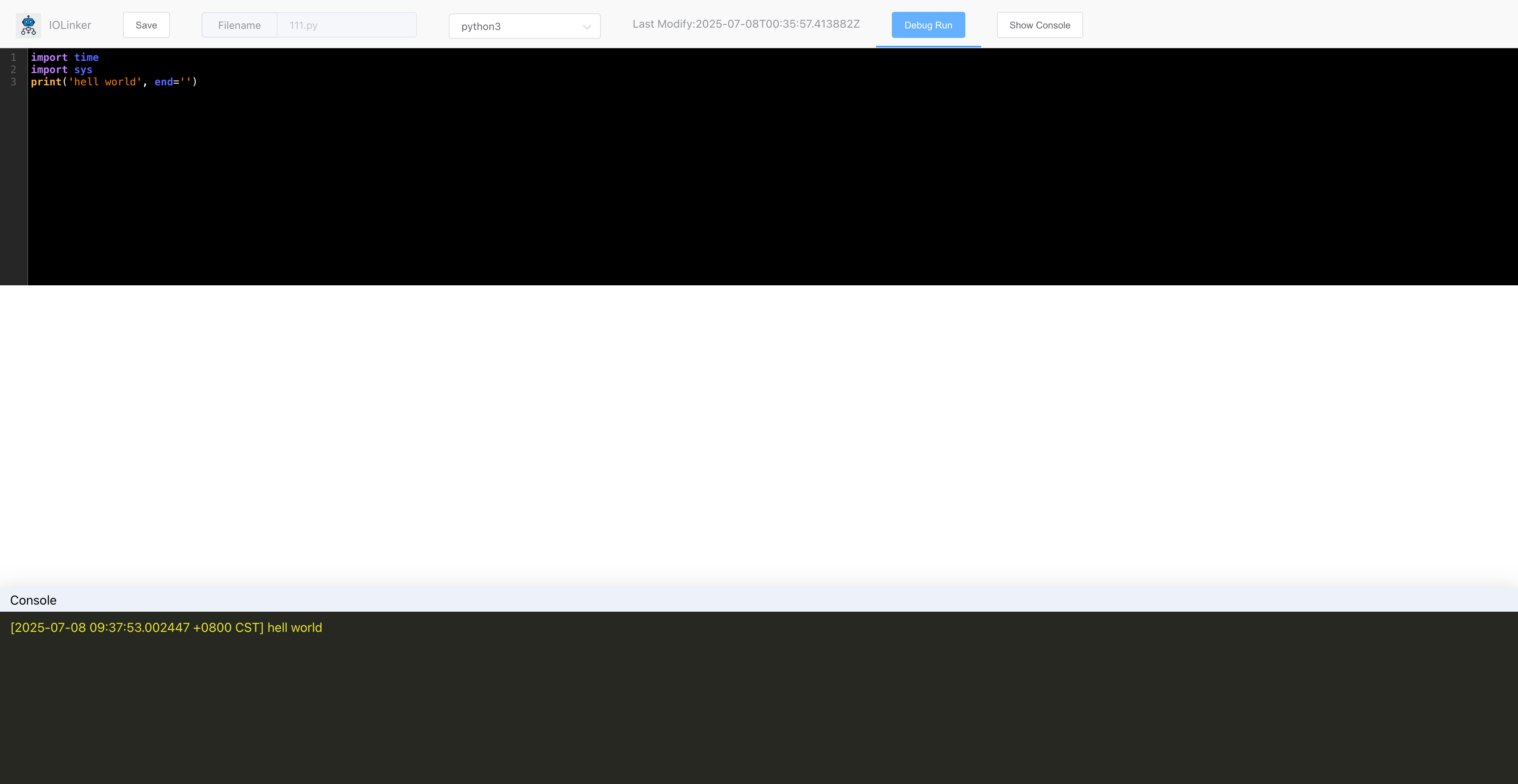
# Code
The code that is currently to be executed.
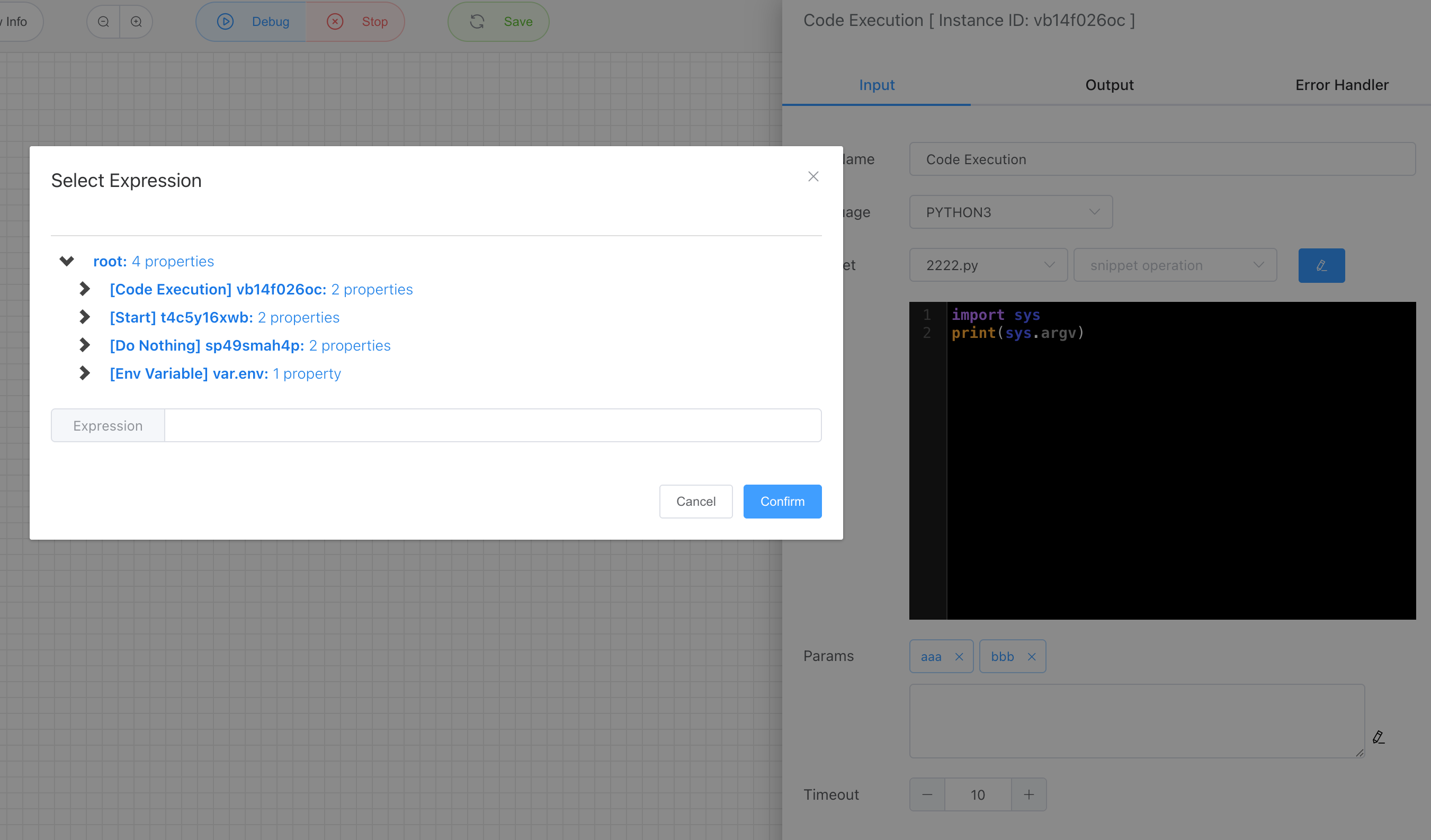
# Params
Here you can pass parameters to the script through sys.argv (python script) or $argv (php script). Of course, you can also use variable expressions to reference previous output as input to the script.
# Timeout
Set the timeout for script execution. If the execution exceeds this time, the system will forcibly terminate it and output an error message:
{
"WorkflowId": 0,
"WorkflowName": "Unknown",
"ExecutionUid": "227174016812625920",
"ErrorAppName": "Code Execution",
"ErrorAppInstId": "oj2ku2mtzs",
"Error": "execute command timeout",
"CreateAt": "xxx"
}
# Error Handler
By default, if an exception occurs during code execution, the default strategy is to throw an exception, and then the entire workflow will report an error and stop running.
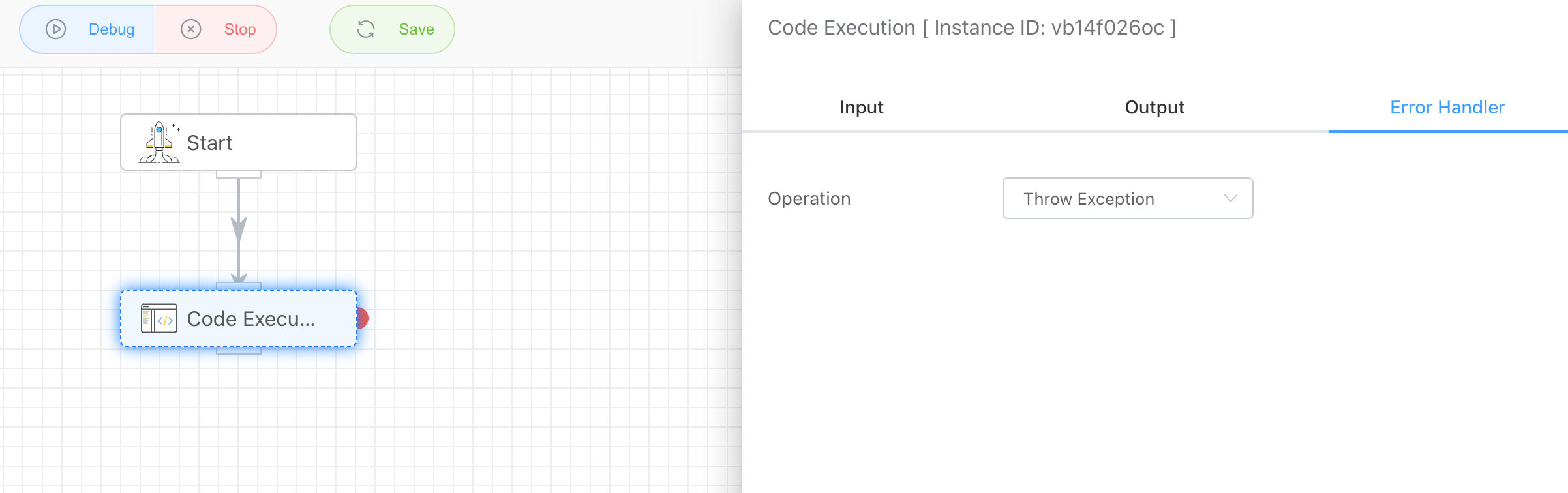
There are currently several strategies:
- Retry
- Throw Exception
- Ignore
- Catch
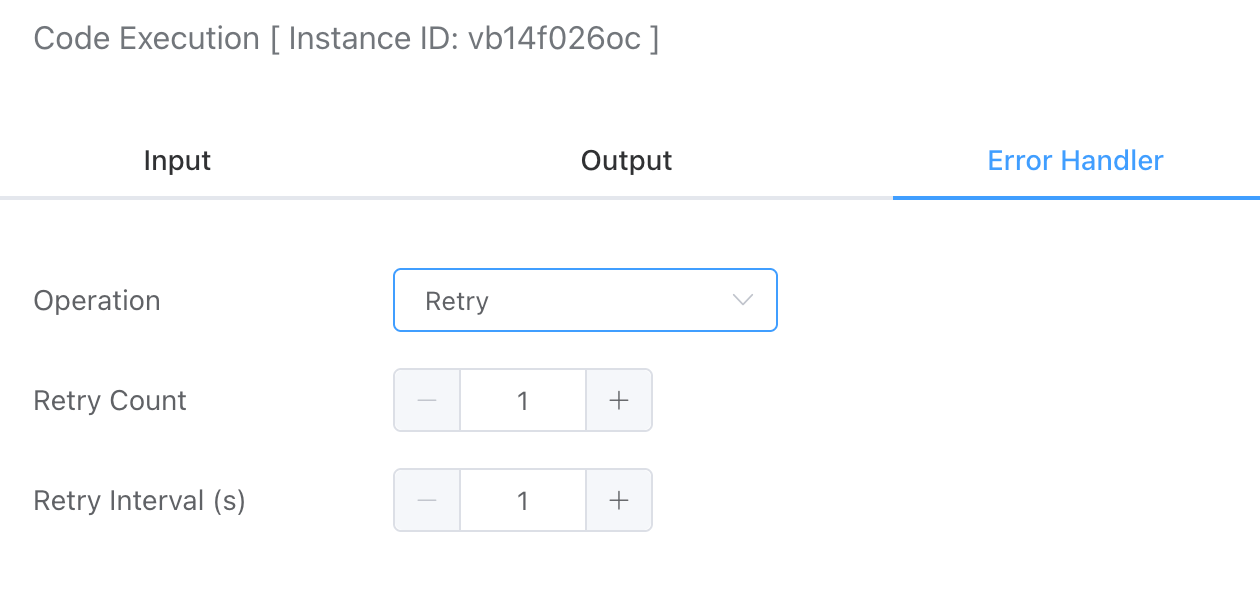
# Retry
The retry strategy can set the number of retries and their intervals when an exception occurs.
# Throw Exception
The default strategy when an exception is thrown directly causes the workflow execution to be abnormal and stop.
# Ignore
If you use the ignore strategy, when an exception occurs, the system will not throw the error, but ignore it and continue to execute.
# Catch
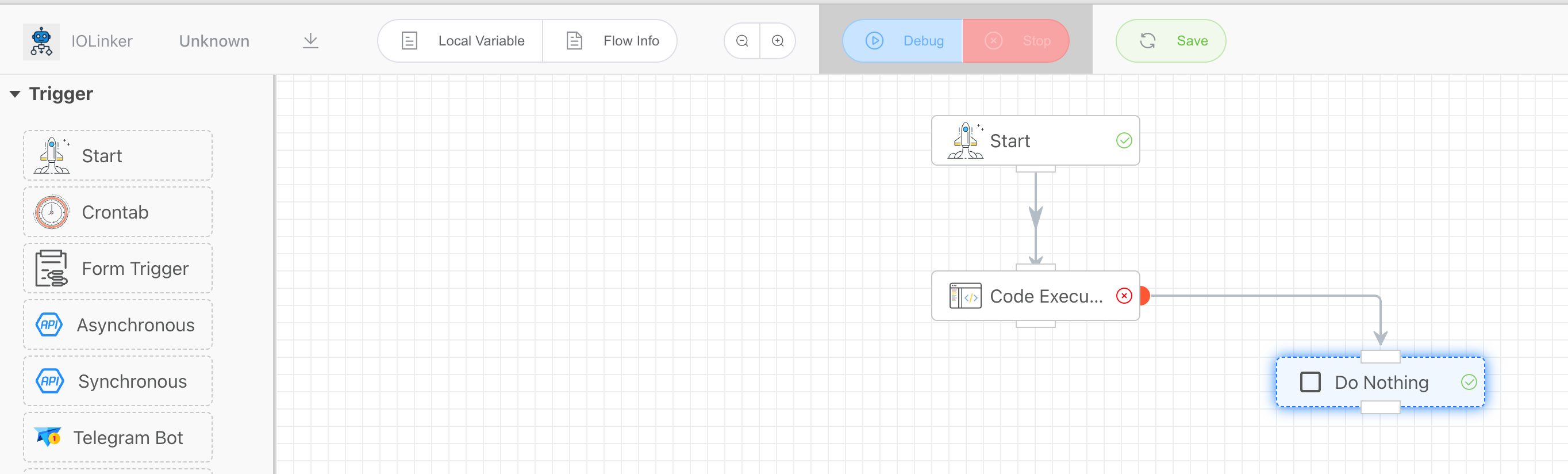
You can set a branch to respond to this exception to handle it. As shown in the figure below, you can capture the exception by connecting from the red origin on the right to other nodes.
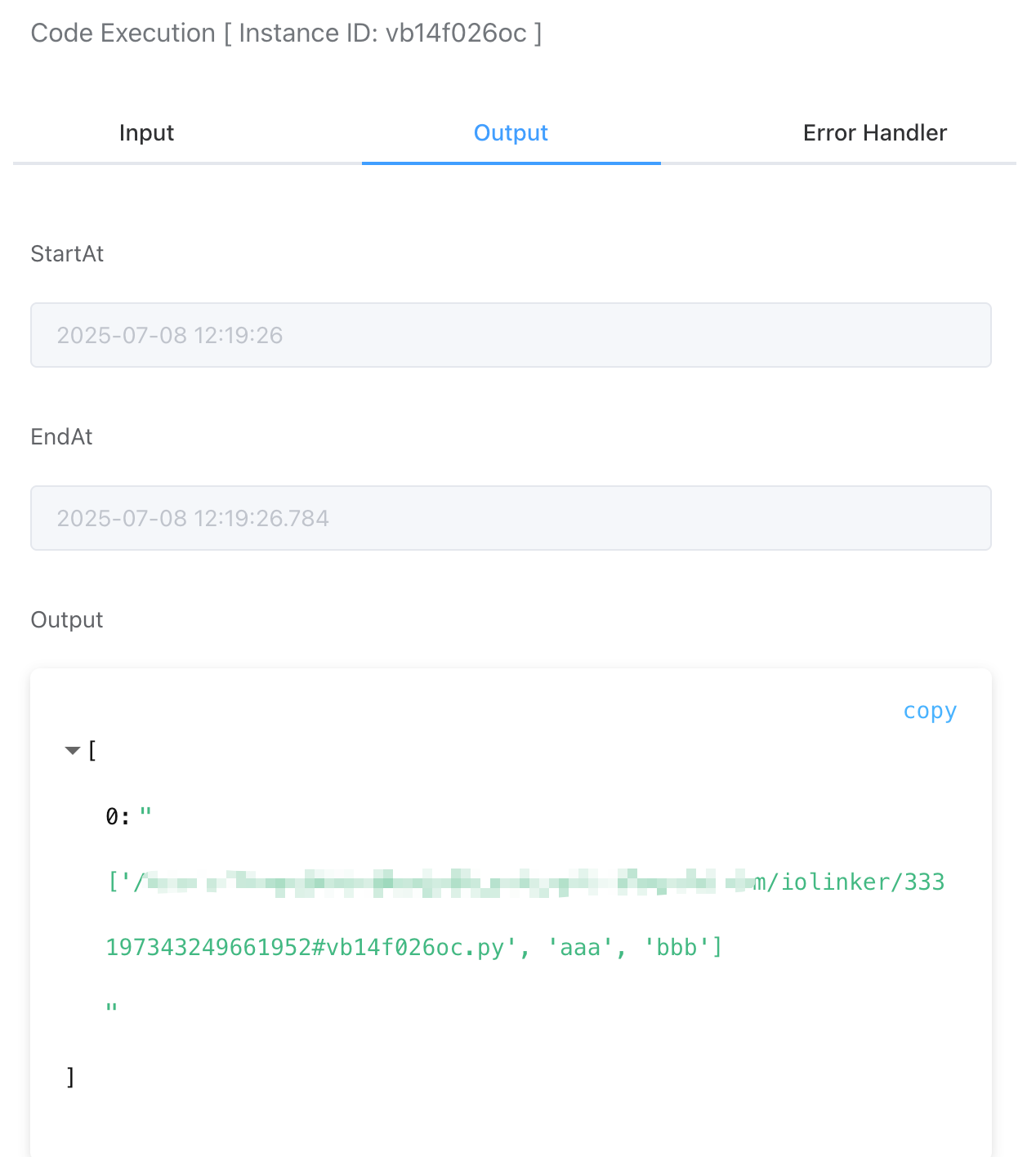
# Output
Here, the terminal output will be used as the output result of the APP. For example:
Python3
Output can be done using
print:print('xxx')Note: The
printmethod includes a newline by default, which can affect the output. If you want to output without a newline, you can use:print('xx', end='')JavaScript
Output can be done using
console.log:console.log('xxx')PHP
Output can be done using
echo:<?php echo "123";